THEORIES AND MODELS IN GEOGRAPHY: ECONOMIC & REGIONAL DEVELOPMENT
Part 3 Economic & Regional Development Theories & Models in Geography for UGC NET Exam
PDF DOWNLOAD LINK IN THE BOTTOM OF THIS POST
Economic & Regional Development MODELS AND THEORIES FOR UGC NET EXAM, THEORIES AND MODELS IN GEOGRAPHY NOTES, MODEL IN GEOGRAPHY STUDY MATERIAL, THEORIES AND MODELS PYQS,
Theories and Models in Geography
Part 1- Geomorphology – Uniformitarianism, Isostasy, Continental Drift Theory, Cavern Formation Theory
Part 2- Climatology – Rainfall Formation Theories, Climatic Classification of Koeppen’s & Thronthwaite’s
Part 2- Oceanography – Theories of Coral Formation, Theories of Origin of Tides
Part 3- Agricultural Geography- Von Thunen’s Model of Land Use, Whittlesey Classification
Part 3- Economic Geography- Industrial Location Theory by Alfred Weber
Part 3- Regional Planning & Development – Economic Growth Model of Rostow, Gunnar Myrdal, O Hirschman, John Friedman, Francois Perroux, Planning Process of MacKaye, Planning Regions of V. Nath, Bhat & Rao, Sen Gupta & Chandrasekhara
Part 4- Population Geography – Population Resource Regions – Ackerman, Theories of Population Growth- Malthusian Theory of Population, Demographic Transition Theory, Theory of Migration- Ravenstein’s Laws, Zelinsky, Push & Pull Theory
Part 5- Settlement and Urban Geography- CENTRAL PLACE THEORY, Economic Location Theory of August Losch, Theories of Urban Urban Morphology- E.W. Burgess, Homer Hoyt, C.D Harris & E.L Ullman
Part 6- Political Geography- Heartland Theory, Rimland Theory
Part 6- Geographical Thought- Philosophical Approaches: Positivism, Pragmatism, Idealism, Realism, New or Critical Realism, Phenomenology, Radicalism, Behaviouralism, Welfare Approach
Agricultural Geography
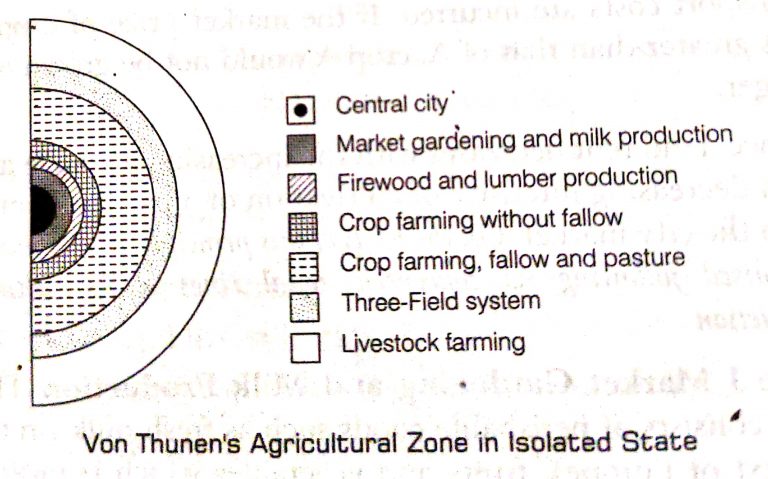
Von Thunen’s Model of Land Use Planning /Agricultural land use/ Location theory (1826)
Von Thunen recognized six concentric zonal rings
Zone I – Market Gardening and Milk Production
Zone II – Firewood and Lumber Production
Zone III – Crop Framing without Fallow
Zone IV – Crop Farming, Fallow and Pastures
Zone V – Three Field System
Zone VI – Livestock Farming
Whittlesey Classification of World Agricultural Region – 1936
Whittlesey has identified the following 13 types of agricultural system regions—
- Nomadic herding
- Livestock ranching
- Shifting cultivation
- Rudimentary tillage
- Intensive subsistence tillage (with paddy dominance)
- Intensive subsistence tillage (without paddy dominance)
- Commercial plantation
- Mediterranean agriculture
- Commercial grain farming
- Commercial livestock and crop farming
- Subsistence crop & livestock farming.
- Commercial dairy farming
- Specialized horticulture
Crop Combination Method
Weaver’s method – 1954
Formula
σ = is the standard deviation
d = difference between actual crop percentage in the study region and the percentage in the theoretical distribution
n = number of crops
Rafiullah’s method – 1956
Formula
Where as
σ = is the deviation
dp = is the positive difference from median value
dn = is the negative difference from median value
n = is number of crops
Doi’s method – 1959
Coppock’s method -1964
- Ricardo – Concept of Economic Rent
J.C. Weaver – Crop – Combination Analysis
Economic Geography/ Industrial Geography
Industrial Location Theory by Alfred Weber (1909)
Book- “Theory of the Location of Industries” (Uber den Standort der Industrien)
- Based on Principle of Least Cost Location
- Ubiquitous raw materials – Water, Air, Soil
- Fixed raw materials
- Pure raw materials
Iso-tim, The line connecting to the equal transportation cost of raw materials or the final product from the source of raw materials to the market.
Isodapanes- The line connecting with equal total transportation cost raw materials and final product transportation), is called isodapane.
Material Index
Regional Planning & Development
- Economic growth and social development – Rostow (1960)
The model postulates that economic growth occurs in five basic stages, of varying length:
The traditional society
The preconditions for take-off
The take-off
The drive to maturity
The age of high mass-consumption
- Cumulative Causation theory Gunnar Myrdal (1956)
Cumulative Causation theory developed by Swedish economist Gunnar Myrdal in the year 1956
In his book ‘Economic Theory & Underdeveloped Regions’, he presented the ‘Cumulative Causation Model’
Concept of ‘Spread’ and ‘Backwash’ effects introduced by Myrdal.
‘Spread’ effects – Growth Inducing Effects – inflow of raw material, new technologies, demand for the agricultural products.
‘Backwash’ effects- Adverse Effects – Withdraw of skilled labour, capital & goods etc.
- Policy of deliberate unbalanced development/Strategy of Unbalanced Growth – Albert O Hirschman (1950s)
- Core-Periphery Theory –John Friedman (1966)
- Growth Pole Theory –Francois Perroux (1955)
- Growth center theory-Bauldevile3
- Planning Process by Benton MacKaye
Process of regional planning
- Perception
- Revelation
- Preparation
- Execution
Planning Regions of India by Regional Planners
- L.S Bhat & V.L.S Prakasa Rao (1964)
11 Major/Macro Region & 51 Minor/Meso Region
- V. Nath (1965)
15 Major Region & 61 Minor Region
- Ashok Mitra Scheme ( 1965):
7 Major Region & 24 Meso Regions & 64 Minor Region
- P. Sen Gupta & Sdasyuk (1968)
7 Major Region & 42 Minor Region
- C.S Chandrasekhar (1972)
13 Major Region & 35 Minor Region
- Towns and Country Planning Organization (1968-1972)
13 Major Region & 35 Minor Region
- Misra’s Scheme (1969)
Misra has suggested four (4) types of of planning region in India
- Metropolitan or city regions (Functional Regions)
- River valley regions
- Axial development region: Along transport lines and irrigation channels.
- Transitional or depressed regions

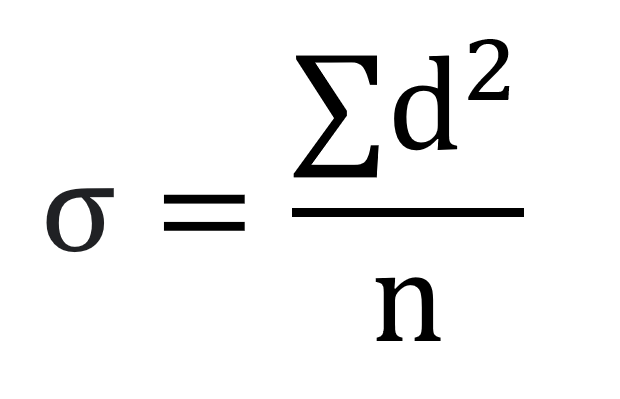
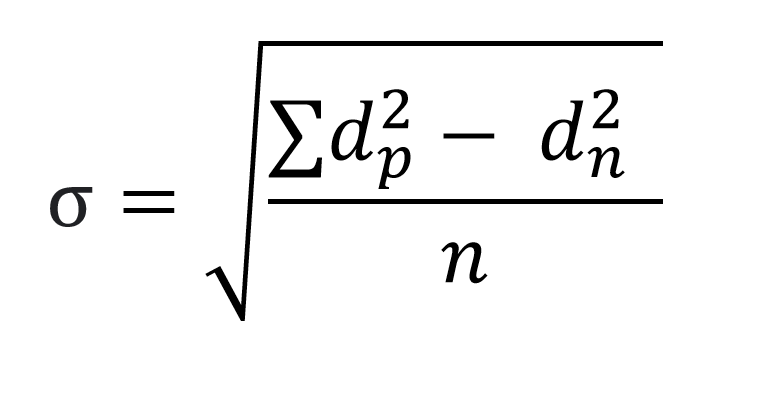

Really usefull
Thank you soo much